Back to Projects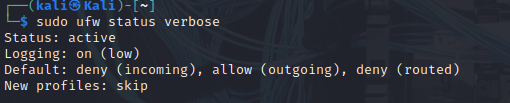
Firewall Setup
✅ Verified CompleteUFW firewall configuration, rule management, and port verification
Network Security•medium priority
Skills Demonstrated
- Firewall Configuration
- Network Security
- UFW
- Port Management
Tools Used
UFWnmapKali Linux
Screenshots



Documentation
View on GitHubFirewall-Setup
A simple project to configure a basic firewall on a Kali Linux machine using UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall). This project focuses on setting secure defaults, allowing specific traffic, denying unnecessary access, and verifying everything with basic scanning.
Lab Goals
- Enable and configure UFW firewall
- Set default rules (deny incoming, allow outgoing)
- Allow HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443) traffic
- Deny SSH (port 22) access
- Verify firewall behavior with
nmap - Capture screenshots for documentation
Commands Used
# Enable UFW sudo ufw enable # Check status sudo ufw status verbose # Allow HTTP traffic (port 80) sudo ufw allow 80/tcp # Allow HTTPS traffic (port 443) sudo ufw allow 443/tcp # Deny SSH traffic (port 22) sudo ufw deny 22/tcp # Show rules with numbers sudo ufw status numbered # Nmap scan to verify open ports nmap 127.0.0.1
Results
- Default Policy:
- Incoming: Deny
- Outgoing: Allow
- Routed: Deny
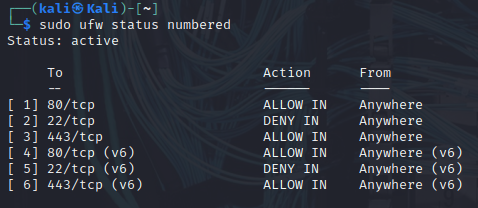
- Allowed Ports:
- 80/tcp (HTTP)
- 443/tcp (HTTPS)
- Denied Ports:
- 22/tcp (SSH)
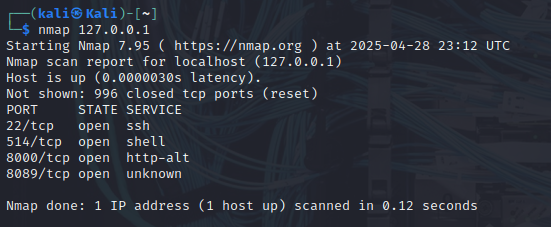
- Nmap Results:
- Some other services were detected due to pre-existing configurations (e.g., 514/tcp, 8000/tcp, 8089/tcp).
Screenshots
Screenshots are stored in the screenshots/ folder:
 - UFW status before rules were applied
- UFW status before rules were applied
 - UFW rules with numbered output showing configured rules
- UFW rules with numbered output showing configured rules
 - Nmap scan results verifying firewall behavior
- Nmap scan results verifying firewall behavior
Lessons Learned
- UFW is a quick and effective way to secure a Linux machine.
- It's important to verify open ports with tools like Nmap even after setting firewall rules.
- Service configurations (e.g., SSH running by default) can affect what ports are open and need to be considered separately from firewall settings.
Improvements for Future Labs
- Explore creating UFW profiles for specific services.
- Set up logging at a higher verbosity to monitor denied traffic.
- Implement rate limiting or connection throttling for brute-force protection.
Part of the "Cybersecurity-Projects" series.
Evidence
- 3 screenshots
- Complete configuration